Creating One Proportion Test with LAMBDA

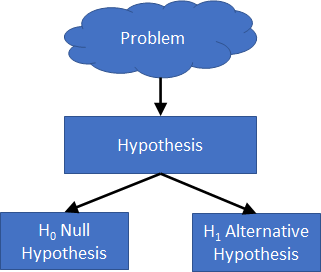
What is One Proportion Test The One Proportion Test compares a sample proportion against a target proportion. For example, you observe that you get 6 heads when you flip a coin 10 times (sample). You expect with a fair coin, the probability of getting heads is 0.5 or 50% of the time (target). The One Proportion Test allows you to assess if the flipped coin is a fair coin based on the observations. The test proves this by statistically comparing the observed proportion of heads to number of flipping 0.6, is equal to the expected proportion 0.5. We write the Null Hypothesis as the observed proportion is equal to the hypothesised proportion. `H_0: p = p_0` And the Alternative Hypothesis is that the observed proportion is not equal to the hypothesised proportion (two-tailed test). `H_1: p != p_0` We could also test if the observed proportion is greater than the hypothesised proportion (left tail test). `H_0: p >= p_0` Or if the observed proportion is less than the hypothesised proporti...